Shading
The shading component describes how the interior of an object will be shaded. This is different from the outline you shaded just above. Shading can be
- Flat
- Linear
- Cylindrical or
- Radial
Use the Quick Editor > Shading tab to adjust the color, brightness and contrast of an object. For more, see Gradient fills.
You can also apply Scaled Texture, Stretched Texture or a Tiled Texture. Shading also includes transparency and transparency mapping. When applied to text geometry, shading changes the background color of the text. For more, see the
Rendering and Shading tutorial.
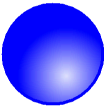
Let's try a bit of shading. Select the circle again and:
- Open the Quick Editor > Shading tab. The circle should still be white inside. Notice that this shows as [no shading] in the Quick Editor. What you are really seeing as white is the white page background showing through
- Select Radial at the bottom of the Quick Editor
- Select the color 1 button and adjust the RGB sliders to create a light blue color.
- Select the color 2 button and adjust the RGB sliders to create a dark blue color.
- Adjust the Transparency slider to see the effect.
- Open the Shading Editor > Fill Settings tab. Move the cross bar with your mouse to adjust the location of the highlight
- Return to the Quick Editor > Shading tab and select Flip
- Assign a texture map to the object
- And why not try a transparency map as well?